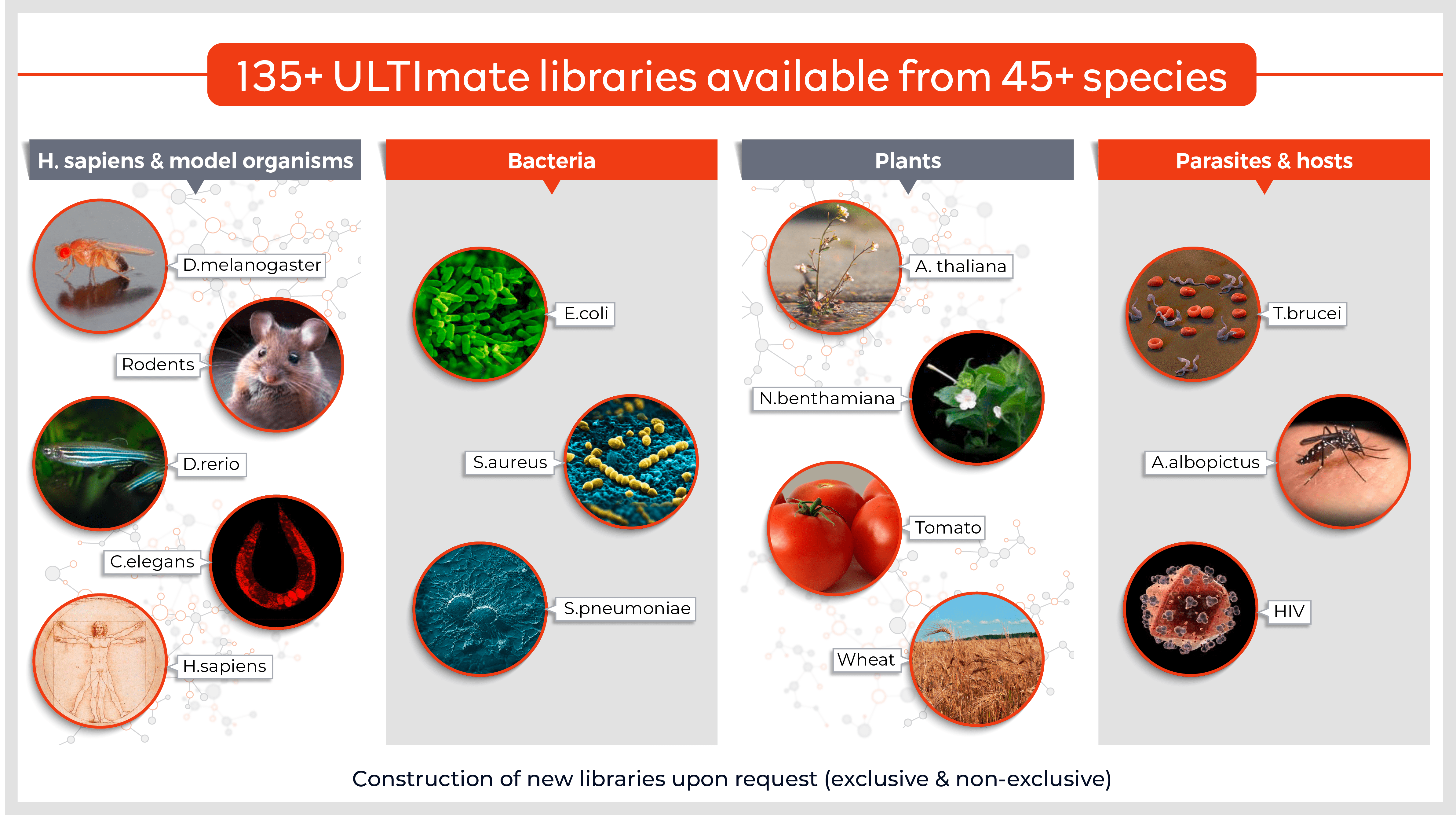
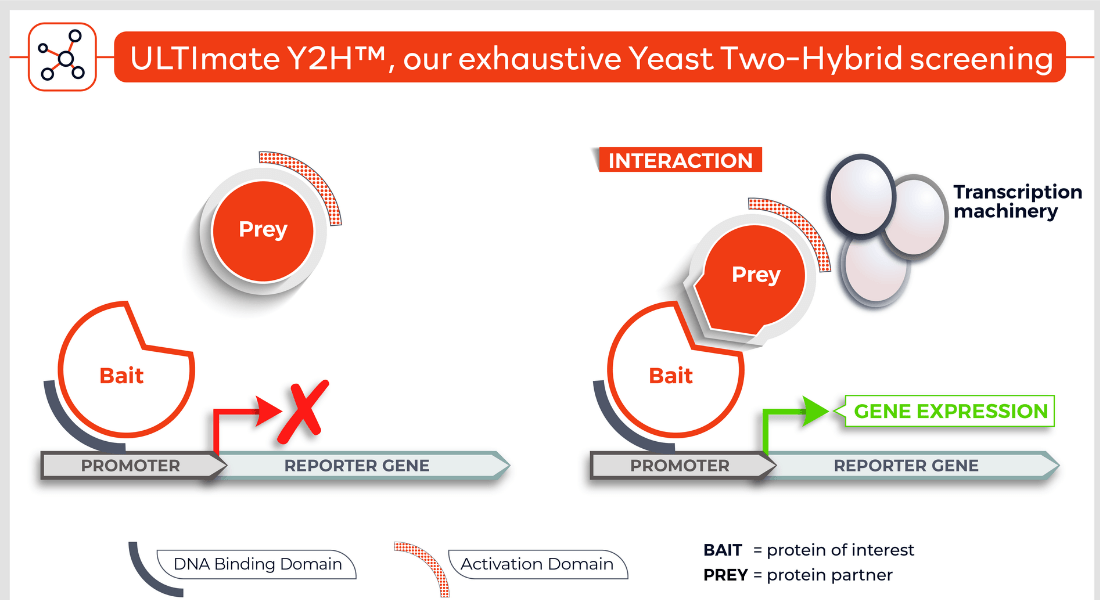
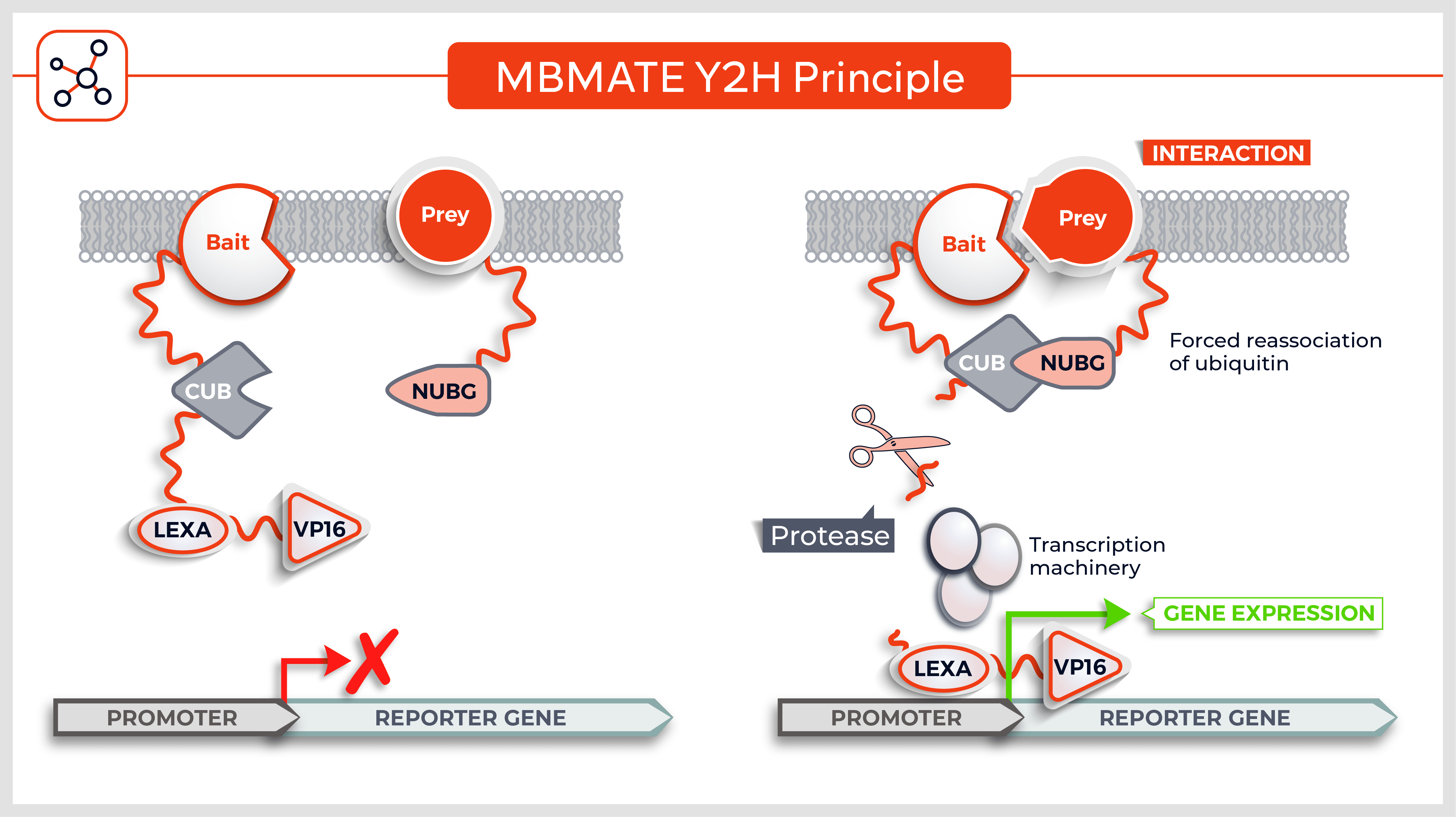
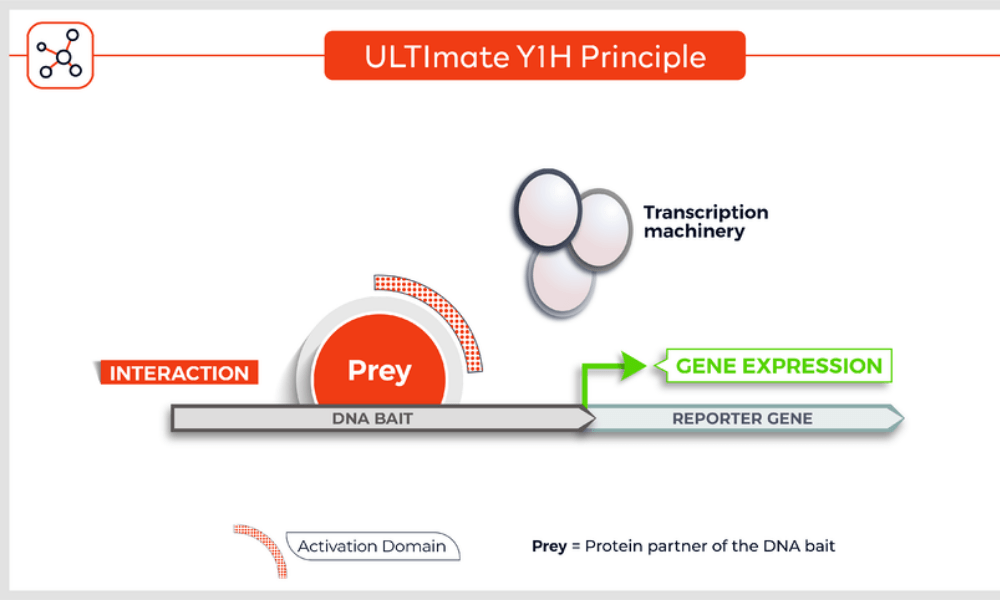
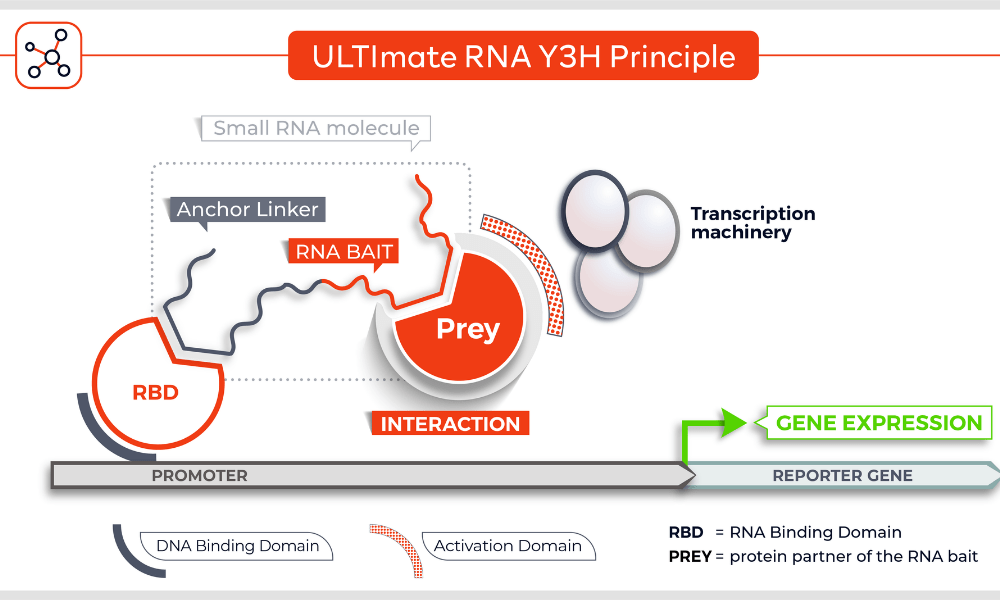
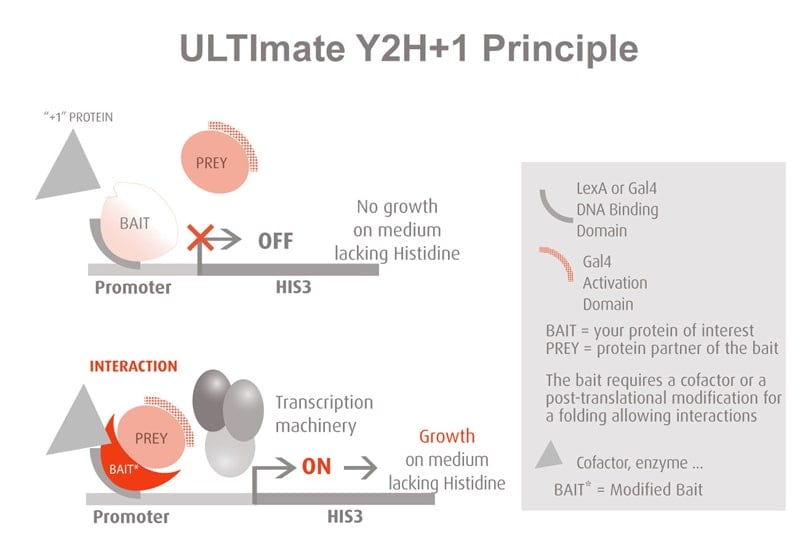
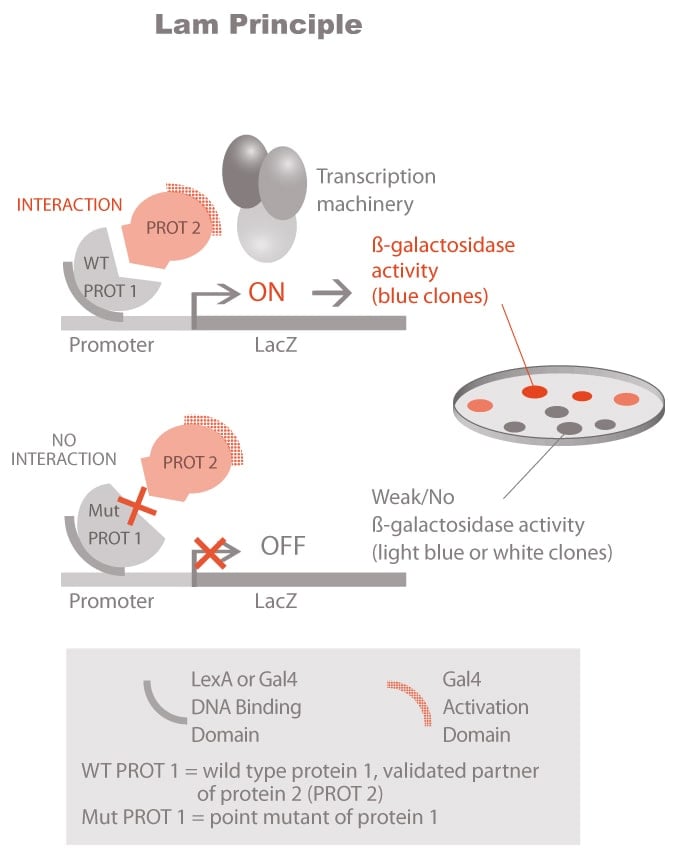
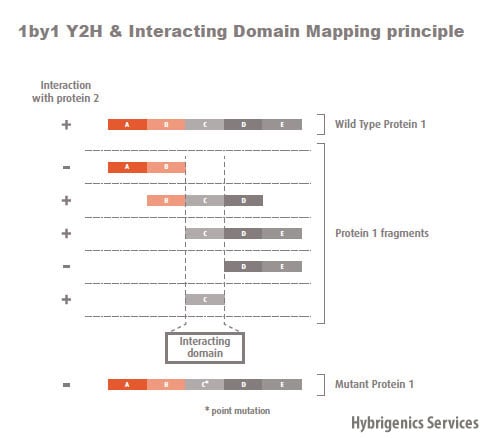
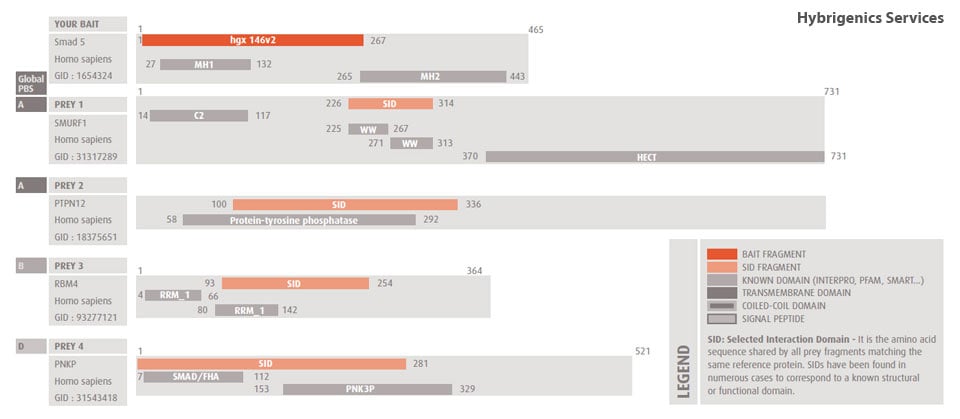
Molecules tested: Soluble proteins
- Full-length proteins, fragments or peptides
- Cytoplasmic and secreted proteins
- Loop regions, cytoplasmic tails and extracellular domains of membrane proteins
Key benefits
- Rapid & exhaustive screening of high-complexity domain-enriched libraries
- Identification of weak and rare binding partners
- Up to 380 positive clones sequenced (5' & 3') in a single screen
- Comprehensive & integrated bioinformatics analysis of results and annotation of functional, structural and interacting domains of the interacting proteins
- Back-up screening strategies included
- High-quality scientific & technical assistance regarding bait design and screening strategy for the best possible outcome